Apprenticeships represent a powerful gateway to professional excellence, combining hands-on experience with structured learning to create skilled, capable workers ready to drive organizational success.
🎯 The Foundation of Apprentice Excellence
Performance benchmarks serve as the compass that guides apprenticeship programs toward measurable success. Without clear standards and expectations, even the most well-intentioned training initiatives can fall short of their potential. Organizations that invest in robust apprentice development frameworks consistently outperform competitors by building talent pipelines that align perfectly with business needs.
The modern apprenticeship landscape has evolved significantly from traditional models. Today’s successful programs integrate technology, mentorship, and data-driven insights to create comprehensive learning experiences. These programs recognize that excellence emerges not from generic training approaches but from carefully calibrated performance indicators that track progress, identify gaps, and celebrate achievements.
Establishing meaningful benchmarks requires understanding both the technical competencies and soft skills necessary for success. Technical proficiency might be measured through practical assessments and certifications, while communication abilities, problem-solving capabilities, and teamwork skills demand more nuanced evaluation methods. The intersection of these competency areas creates the complete picture of apprentice readiness.
📊 Defining Performance Benchmarks That Matter
Effective performance benchmarks must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Generic goals like “improve skills” provide little actionable guidance. Instead, successful programs establish clear milestones such as “complete three supervised installations with 95% accuracy within the first quarter” or “demonstrate proficiency in five core software applications by month six.”
The architecture of meaningful benchmarks begins with comprehensive job analysis. What tasks will apprentices perform upon completion? What knowledge domains must they master? Which workplace behaviors separate exceptional performers from average ones? Answering these questions creates the foundation for standards that truly prepare apprentices for their future roles.
Essential Components of Benchmark Systems
Competency frameworks should encompass multiple dimensions of performance. Technical skills form the obvious starting point, but emotional intelligence, adaptability, and continuous learning mindset prove equally critical in today’s dynamic work environments. Organizations that assess only technical proficiency often find their graduates unprepared for real-world complexity.
Progression pathways provide apprentices with clear visibility into their development journey. Breaking the overall program into distinct phases with specific accomplishments for each stage creates motivational momentum. Apprentices can see their advancement, understand what comes next, and take ownership of their growth trajectory.
Feedback mechanisms must be embedded throughout the benchmark system. Regular check-ins, formal reviews, and continuous feedback loops ensure apprentices understand their current standing and receive guidance for improvement. Without consistent feedback, even well-designed benchmarks lose their effectiveness as developmental tools.
🚀 Implementing Structured Assessment Frameworks
Assessment strategies should balance multiple evaluation methods to capture comprehensive performance data. Written examinations test knowledge retention and theoretical understanding. Practical demonstrations reveal applied skills and problem-solving abilities. Peer reviews and supervisor observations add perspectives on collaboration and workplace integration.
Digital platforms have revolutionized how organizations track and manage apprentice progress. Learning management systems, skills tracking applications, and performance dashboards provide real-time visibility into individual and cohort advancement. These tools transform assessment from periodic snapshots into continuous monitoring that enables proactive intervention.
Portfolio development offers apprentices a powerful way to document their growing capabilities. By compiling work samples, project descriptions, certifications, and reflection statements, apprentices create tangible evidence of their journey. These portfolios serve dual purposes—supporting internal assessment while providing career advancement tools apprentices can leverage beyond their training.
Creating Meaningful Evaluation Rubrics
Detailed rubrics remove ambiguity from performance expectations. Rather than subjective judgments about quality, rubrics specify exactly what distinguishes novice, developing, proficient, and exemplary performance across each competency area. This clarity benefits both apprentices who understand standards and assessors who apply consistent criteria.
Rubrics should include behavioral indicators that make abstract concepts concrete. Instead of rating “communication skills” generically, effective rubrics describe specific observable behaviors: “Asks clarifying questions when receiving instructions,” “Provides clear status updates without prompting,” or “Adapts communication style to different audiences.”
💡 Leveraging Mentorship to Accelerate Growth
Even the most sophisticated benchmark systems cannot replace human guidance and support. Mentors transform performance standards from abstract expectations into practical wisdom, modeling excellence while providing personalized coaching that addresses individual apprentice needs and learning styles.
Effective mentorship programs match apprentices with experienced professionals who possess both technical expertise and coaching ability. The best mentors understand that their role extends beyond knowledge transfer—they inspire confidence, provide encouragement during setbacks, and help apprentices navigate the unwritten rules of workplace culture.
Structured mentorship protocols ensure consistency across apprentice experiences. Regular meeting schedules, conversation frameworks, and documentation practices create accountability while preserving the flexibility mentors need to address individual circumstances. Organizations that formalize mentorship practices while allowing relationship authenticity achieve the strongest outcomes.
Building Mentor Capacity and Capability
Mentors themselves require training and support to maximize their effectiveness. Many technical experts lack formal coaching skills or struggle to articulate the tacit knowledge that guides their own excellence. Investing in mentor development pays dividends through enhanced apprentice outcomes and increased mentor satisfaction.
Recognition systems that acknowledge mentor contributions reinforce the value organizations place on this critical role. Whether through formal awards, compensation adjustments, or career advancement opportunities, recognizing mentorship excellence encourages continued engagement and attracts high-caliber professionals to these positions.
📈 Data-Driven Decision Making for Continuous Improvement
Organizations that excel in apprentice development treat their programs as living systems requiring constant refinement. Performance data reveals patterns about which approaches work, where bottlenecks occur, and how different cohorts respond to various interventions. This intelligence informs strategic adjustments that compound effectiveness over time.
Tracking metrics should extend beyond individual apprentice performance to encompass program-level indicators. Completion rates, time-to-proficiency, post-program retention, and employer satisfaction scores provide insights into systemic strengths and weaknesses. Comparative analysis across cohorts highlights whether changes improve outcomes or require further modification.
Predictive analytics represent the frontier of apprenticeship optimization. By identifying early warning signs that correlate with future struggles, organizations can implement targeted supports before apprentices fall significantly behind. Machine learning algorithms can detect subtle patterns human observers might miss, enabling increasingly personalized interventions.
Creating Feedback Loops That Drive Excellence
Stakeholder input enriches quantitative performance data with qualitative context. Regular surveys capturing apprentice perspectives on program strengths, challenges, and opportunities ensure their voices shape improvements. Similarly, supervisor and mentor feedback reveals implementation realities that may differ from program intentions.
Alumni perspectives provide invaluable insights once apprentices transition to independent roles. Their reflections on which aspects of training proved most valuable and where they felt unprepared guide curriculum adjustments. Organizations that maintain relationships with alumni create continuous feedback channels that keep programs relevant and effective.
🎓 Integrating Formal Credentials and Certifications
Industry-recognized certifications add credibility and portability to apprenticeship achievements. While internal performance benchmarks measure progress against organizational standards, external credentials validate capabilities according to broader industry norms. This dual approach maximizes both immediate organizational value and long-term apprentice career prospects.
Strategic credential selection requires understanding which certifications carry genuine weight within specific industries. Not all credentials offer equal value—some represent true competency validation while others serve primarily as revenue generators for issuing organizations. Research into employer preferences and industry standards guides wise investments.
Preparation for certification examinations should integrate naturally into apprenticeship activities rather than creating separate study burdens. When training content aligns with certification requirements, apprentices develop job-ready skills while simultaneously preparing for credential assessments. This integration eliminates redundancy and maximizes learning efficiency.
🌟 Cultivating Soft Skills and Professional Behaviors
Technical proficiency alone rarely determines long-term career success. Professionals who combine technical excellence with strong communication, collaboration, critical thinking, and adaptability skills advance further and contribute more comprehensively than those focused exclusively on technical domains.
Soft skills development requires intentional design rather than assuming these capabilities emerge naturally. Structured opportunities for presentation practice, team projects, conflict resolution exercises, and client interaction gradually build confidence and competence. Feedback specifically addressing these dimensions helps apprentices understand their importance and monitor their growth.
Workplace professionalism encompasses punctuality, initiative, accountability, and ethical decision-making—qualities that significantly impact team dynamics and organizational culture. Explicitly teaching and assessing professional behaviors communicates their importance while providing apprentices with frameworks for navigating workplace expectations that may differ from previous environments.
Developing Emotional Intelligence and Resilience
Self-awareness, emotional regulation, empathy, and relationship management constitute the foundation of emotional intelligence. These capabilities enable professionals to collaborate effectively, navigate workplace stress, receive constructive criticism productively, and maintain motivation through challenges. Organizations that develop emotional intelligence alongside technical skills build more resilient, adaptable workforces.
Resilience training prepares apprentices for the inevitable setbacks and failures that accompany skill development. Learning to view mistakes as growth opportunities rather than personal deficiencies creates healthier learning mindsets. Techniques for managing stress, seeking support, and maintaining perspective during difficult periods serve apprentices throughout their careers.
🔄 Creating Pathways from Apprentice to Expert
Successful apprenticeship programs don’t end abruptly upon completion but create clear progression pathways that extend throughout careers. Defining advancement stages beyond initial proficiency—from competent practitioner to advanced specialist to master craftsperson—provides continued motivation and development structure.
Leadership pipeline development ensures organizations cultivate not just skilled workers but future supervisors, mentors, and program leaders. Identifying apprentices with leadership potential early enables targeted development experiences that prepare them for these expanded roles. This approach creates self-sustaining systems where today’s apprentices become tomorrow’s mentors.
Continuous learning cultures recognize that initial training represents the beginning rather than the culmination of professional development. Providing access to advanced training, conference attendance, professional association membership, and continuing education opportunities signals organizational investment in long-term growth. These cultures retain talent by offering compelling career trajectories.
🛠️ Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Resource constraints frequently challenge apprenticeship program ambitions. Time demands on mentors, costs associated with training materials and assessments, and opportunity costs of apprentice productivity during learning periods create real pressures. Successful organizations address these challenges through creative solutions like peer mentoring, digital resource libraries, and phased responsibility increases that balance learning with contribution.
Consistency across supervisors and locations presents another common obstacle, particularly in geographically distributed organizations. Standardized training materials, regular calibration sessions among assessors, and centralized program management help maintain quality while respecting necessary local adaptations. Technology enables coordination that would have been impossible in previous eras.
Engagement challenges arise when apprentices feel overwhelmed, under-supported, or disconnected from program purpose. Regular check-ins, peer cohort connections, and transparent communication about progression help maintain motivation. Celebrating milestones and recognizing achievements creates positive momentum that sustains engagement through difficult learning periods.
✨ Measuring Return on Investment and Program Value
Quantifying apprenticeship ROI justifies program investments and secures ongoing organizational support. Metrics might include time-to-productivity comparisons between apprentices and traditional hires, retention rate differences, quality indicators, and customer satisfaction scores. Financial calculations should account for both direct program costs and avoided expenses of alternative talent acquisition strategies.
Intangible benefits complement quantitative ROI analysis. Enhanced employer brand reputation, strengthened community relationships, improved workplace culture, and increased innovation capacity all contribute value that defies simple measurement yet significantly impacts organizational success. Comprehensive program evaluation captures both tangible and intangible returns.
Long-term tracking reveals compounding benefits as apprentice cohorts advance through careers. Organizations that maintain relationships with alumni can document career progression, leadership emergence, and continued organizational contribution. These longitudinal perspectives demonstrate how initial investments yield returns across decades rather than merely quarters or years.
🌐 The Future of Apprentice Development
Emerging technologies continuously reshape possibilities for apprentice training and assessment. Virtual reality simulations provide safe environments for practicing dangerous or expensive procedures. Artificial intelligence enables personalized learning paths that adapt to individual progress patterns. Blockchain credentials create verifiable, portable records of competency achievement.
Remote and hybrid work models demand reimagined apprenticeship approaches that balance virtual connection with hands-on experience. Organizations pioneering distributed apprenticeships develop innovative solutions for building relationships, facilitating skill development, and maintaining engagement across distance. These adaptations expand access while creating new implementation challenges.
Cross-industry collaboration strengthens apprenticeship ecosystems through shared standards, credential portability, and collective advocacy. Industry associations, educational institutions, and employer consortiums increasingly coordinate efforts to elevate apprenticeship quality and recognition. These partnerships create rising tides that lift all participants.
💪 Empowering Apprentices as Partners in Their Development
Apprentices who take ownership of their learning progress faster and retain knowledge more effectively than passive participants. Creating structures for self-assessment, goal-setting, and reflection develops metacognitive skills that enable lifelong learning. Apprentices become partners in their development rather than recipients of training.
Choice architecture within programs respects individual learning preferences and career interests. Offering electives, specialization tracks, or project options acknowledges that even within defined competency frameworks, multiple valid paths exist. This flexibility increases engagement while developing decision-making capabilities apprentices will need throughout their careers.
Transparent communication about program rationale helps apprentices understand why specific benchmarks exist and how each component contributes to overall preparation. This context transforms compliance-based participation into meaningful engagement. When apprentices grasp the purpose behind expectations, they invest more deeply in meeting and exceeding standards.
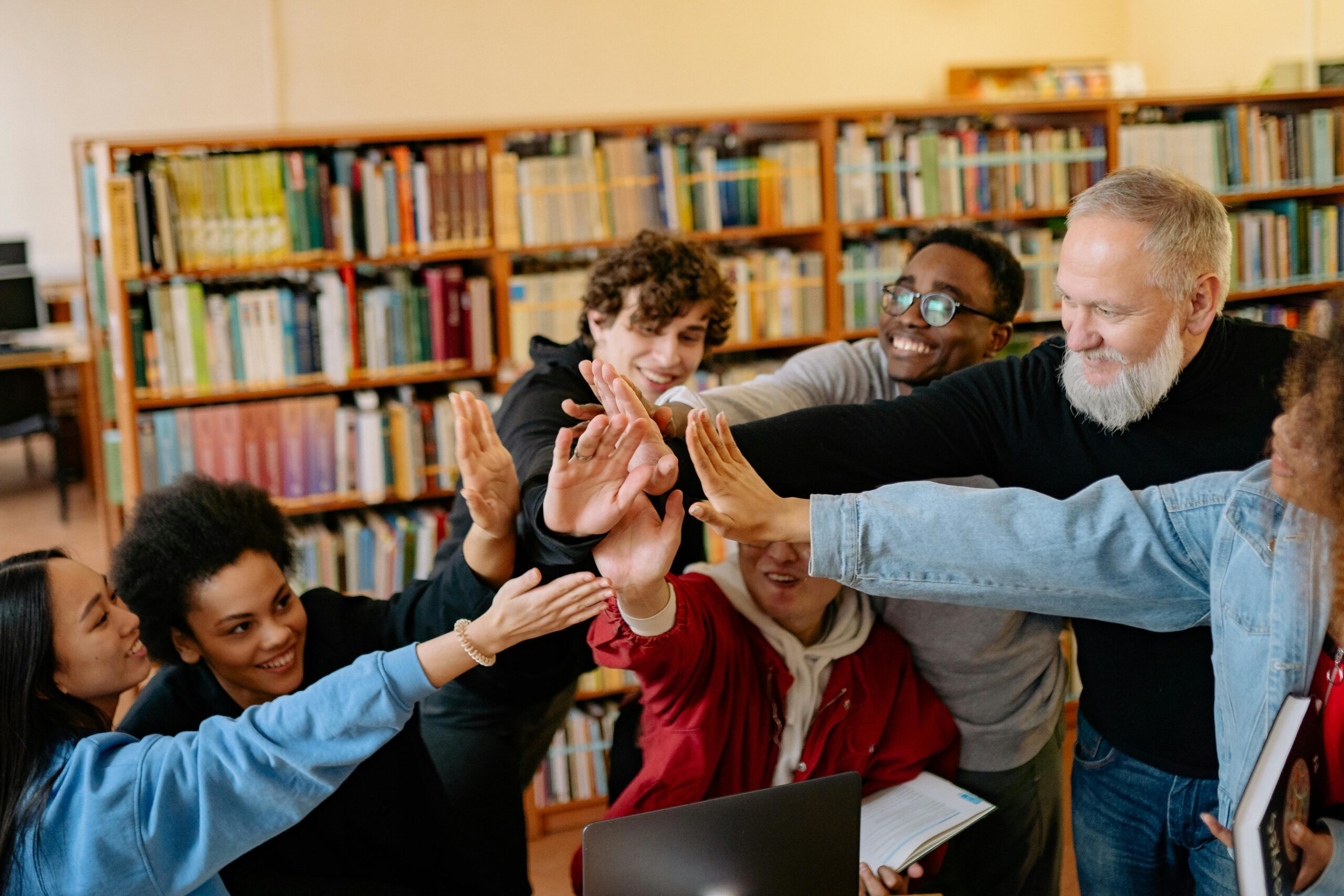

🎖️ Recognizing Excellence and Celebrating Achievement
Recognition systems that acknowledge both effort and achievement sustain motivation throughout apprenticeship journeys. Public celebrations of milestone completions, spotlight features of exemplary work, and formal graduation ceremonies create memorable moments that reinforce accomplishment. These recognitions signal organizational pride in apprentice development.
Peer recognition often carries special weight, as apprentices value acknowledgment from colleagues navigating similar challenges. Creating opportunities for apprentices to nominate and celebrate each other builds cohort cohesion while reinforcing desired behaviors. These peer-driven recognitions complement formal supervisor assessments.
Connection to organizational impact helps apprentices see how their developing capabilities contribute to broader mission fulfillment. Sharing customer testimonials, showcasing completed projects, or highlighting problem-solving contributions demonstrates that apprentices add meaningful value even while learning. This connection to purpose sustains engagement and builds professional identity.
Mastering apprentice success requires intentional design, consistent implementation, and continuous refinement of performance benchmarks that guide development from novice to expert. Organizations that invest in comprehensive apprenticeship programs grounded in clear standards, supportive mentorship, and data-driven improvement create sustainable competitive advantages through talent pipelines perfectly aligned with strategic needs. The journey from apprentice to accomplished professional becomes a transformative experience that benefits individuals, organizations, and entire industries when approached with commitment to excellence and genuine investment in human potential.
Toni Santos is a historian and researcher specializing in the study of early craft guild systems, apprenticeship frameworks, and the regulatory structures that governed skilled labor across preindustrial Europe. Through an interdisciplinary and documentary-focused lens, Toni investigates how trades encoded and transmitted expertise, maintained standards, and controlled access to knowledge — across regions, guilds, and regulated workshops. His work is grounded in a fascination with craft trades not only as economic systems, but as carriers of institutional control. From apprenticeship contract terms to trade secrecy and guild inspection protocols, Toni uncovers the legal and operational tools through which guilds preserved their authority over skill transmission and labor movement. With a background in labor history and institutional regulation, Toni blends legal analysis with archival research to reveal how guilds used contracts to shape training, restrict mobility, and enforce quality standards. As the creative mind behind lynetora, Toni curates illustrated case studies, comparative contract analyses, and regulatory interpretations that revive the deep institutional ties between craft, control, and credential systems. His work is a tribute to: The binding structures of Apprenticeship Contracts and Terms The guarded methods of Knowledge Protection and Trade Secrecy The restrictive presence of Labor Mobility Constraints The layered enforcement of Quality Control Mechanisms and Standards Whether you're a labor historian, institutional researcher, or curious student of craft regulation and guild systems, Toni invites you to explore the hidden structures of skill governance — one contract, one clause, one standard at a time.